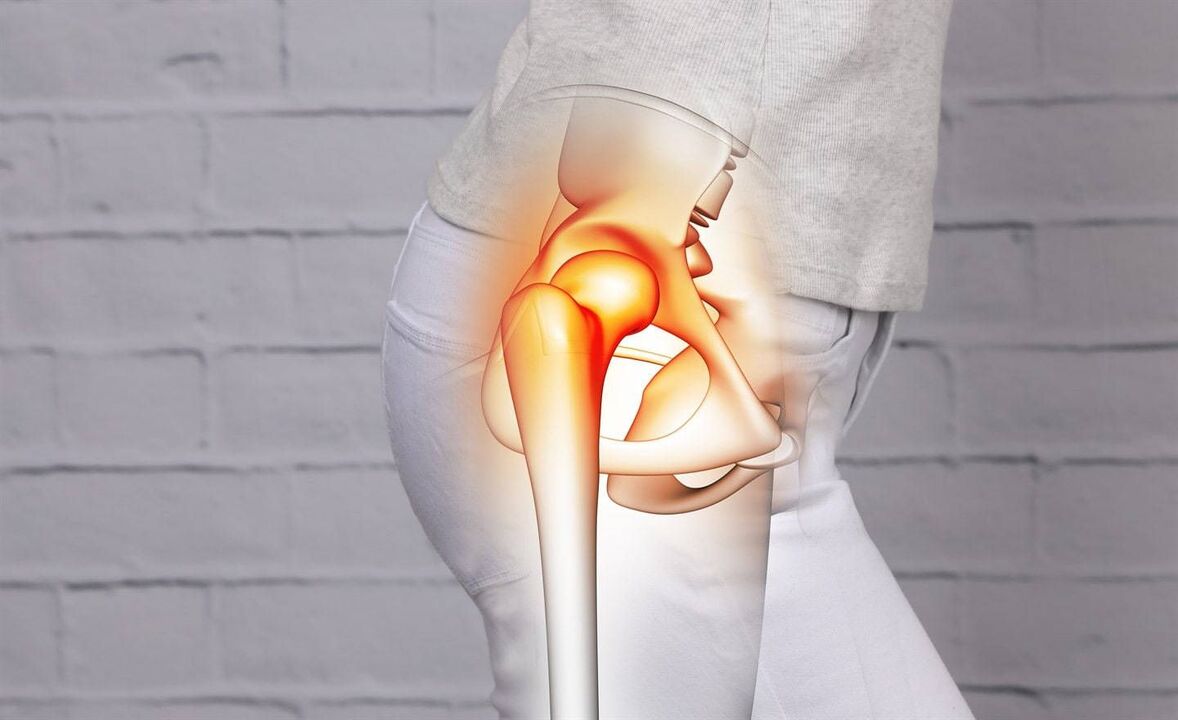
The human hip joints are under enormous stress. Walking, lifting and carrying heavy objects, jumping, running, bending, other physical exercises, and even excess weight put pressure on the musculoskeletal system. Pain in the hip joint reduces its functionality, interferes with free movement and causes suffering to the patient not only during movement, but also at rest. It is very important not to ignore the pain and at the first symptoms of discomfort, immediately seek help from qualified doctors. Orthopedists, traumatologists, surgeons, neurologists and many other specialists jointly evaluate the symptoms, look for the causes and treat pain in the hip joint.
causes of pain
There are a large number of diseases and pathological conditions that can be accompanied by pain. Pain in the hip joint on the left or right side can be caused by injuries, inflammatory and infectious pathologies, various degenerative processes, problems with the supply of useful minerals to bone tissue, etc.
Injuries to the soft tissues and osteoarticular structures in the hip area are the most common cause of discomfort. These include:
- bruises;
- penetrating wounds;
- fracture of the femoral neck;
- hip dislocation;
- Fractures of the acetabulum and the upper part of the femur (so-called pertrochanteric fractures).
Of the traumatic causes, damage to the ligamentous apparatus (sprain, tear, rupture) is less common. In most cases, they are caused by serious injuries that the patient sustained as a result of an accident, prolonged exposure to debris, or due to performing extreme stunts.
Infectious, inflammatory and degenerative diseases that can cause hip joint pain include:
- various forms of arthritis (infectious, aseptic, rheumatoid);
- panarthritis – total purulent inflammation of the hip joint;
- osteomyelitis;
- tuberculosis of the hip joint;
- coxarthrosis and other types of osteoarthritis;
- bursitis;
- aseptic necrosis of the femoral head, including Perthes disease;
- chondromatosis;
- trochanteritis.
Other pathological factors include:
- congenital anomalies of the development of the hip joint (dysplasia, congenital dislocation of the hip, shortening of the limbs);
- various neoplasms of a malignant and benign nature;
- sciatic nerve neuropathy;
- osteochondrosis, scoliosis, intervertebral hernia and other diseases of the spine.
Pain in the hip joint when walking or lying down may indicate excessive stress on the musculoskeletal system. Discomfort may occur after strength training, carrying heavy objects, or walking or standing for long periods of time. The risk group includes athletes, fans of extreme sports, porters, teachers, lecturers, salespeople, couriers, etc.
Other causes of severe pain in the hip joint when walking and at rest can be:
- excess weight, which significantly increases pressure on the joints;
- posture disorders;
- irrational use of certain medications;
- diabetes;
- neuropsychiatric disorders.
The largest number of patients with pain of varying intensity in this area are people over 50 years of age. This is explained by age-related changes in the periarticular tissues and in the joint itself. It has been observed that women suffer from pain more frequently than men.
Types and symptoms of hip pain
The main manifestation is unpleasant sensations in the joint area of various types: sharp, pulsating, painful, dull, cutting, etc. The location and intensity of the pain syndrome depend on the initial disease and the patient's health characteristics (presence of concomitant pathologies, excess weight, risk factors). Often, the pain syndrome spreads to the surrounding structures and radiates to the extremities, the sacrum and coccyx area, and the lower back.
Symptoms that may accompany hip pain include:
- swelling of the tissue in the joint area;
- creaking, clicking and other sounds when moving;
- limited mobility;
- numbness, decreased sensation in the leg;
- sensation of heat, pulsations in the damaged area;
- lameness, dragging of the leg;
- shortening of the limb;
- bruises;
- elevated body temperature.
Pain in the hip joint, radiating to the lower back, leg, groin and sacral area, may indicate ankylosing spondylitis. This disease is also accompanied by stiffness of movement, discomfort in the knee and periodic "lumbago. "Symmetrical pain in the hip area, combined with conjunctivitis and damage to the genitourinary system, may be a sign of Reiter's syndrome.
The clinical picture is determined by the primary disease or injury. In mild cases, the patient has limited movement, but the ability to hold the leg remains. In case of severe bruises, fractures, dislocations and severe forms of infectious and inflammatory diseases, support of the affected leg is impossible; The patient can only move with the help of an auxiliary point or cannot walk at all.
Diagnosis
To establish the exact cause of pain, other symptoms of the primary disease/injury and select an effective treatment regimen, a comprehensive examination is carried out.
First, a physical examination is performed. The doctor evaluates external signs of pathology, palpates the joint area, asks detailed questions about the nature of the complaints, the time and circumstances of their appearance, etc. The specialist also needs to know previous surgical interventions and injuries, existing chronic pathologies (including those that are not directly related to the musculoskeletal system), lifestyle, etc.
A comprehensive objective exam includes:
- ultrasound examination of the hip joint (ultrasound);
- pelvis x-ray in two projections;
- MRI or CT scan (according to indications);
- joint puncture;
- diagnostic arthroscopy;
- laboratory tests (general clinical blood and urine tests, biochemistry, rheumatoid factor analysis, tumor markers, etc. ).
The exact list of procedures is determined by the doctor based on the medical history, characteristics of the patient's current condition and the expected diagnosis.
Hip pain treatment
Medical care tactics depend on the cause of the pain. In case of sprains and bruises, the joint is immobilized, the patient is prescribed pain relievers and strict bed rest is imposed. In case of dislocation, the joint is realigned and the limb is then fixed in a stationary position. For fractures, skeletal traction, cast immobilization, or the use of special structures are indicated.
For hip pain caused by inflammatory or infectious causes, treatment may include:
- antibacterial medications;
- anti-inflammatory medications;
- corticosteroid hormones;
- analgesics;
- chondroprotectors;
- cytostatics;
- ointments, creams and other topical agents that stimulate blood flow;
- vitamin complexes;
- synovial fluid substitutes.
The patient is required to receive a complex of physiotherapy, physiotherapy and massage necessary to restore motor activity, normalize joint nutrition and eliminate signs of inflammation. This may include:
- massage;
- ultrahigh frequency;
- laser therapy;
- electrophonophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- shock wave therapy;
- hydrotherapy and swimming.
The patient's lifestyle is corrected: prevention of obesity, normalization of physical activity, limitation of strength loads, etc.
If conservative treatment does not have the desired effect or the primary disease is treated only surgically, surgical intervention is prescribed. It is performed through an open approach or through an arthroscopic technique. As part of the surgical treatment of diseases that cause pain in the hip joint, the following can be done:
- reduction of dislocations;
- reconstruction of individual joint structures;
- endoprostheses;
- tumor removal;
- fixed fixation of the joint (arthrodesis);
- arthroplasty.
These and other methods of surgical treatment are selected according to the diagnosis and characteristics of the patient's current condition. After surgical treatment, the patient undergoes a rehabilitation course.
Complications
Pain in the hip joint cannot be ignored. Even minor and temporary discomfort can lead to the development of serious diseases in the future. In complex cases, the consequences can be irreversible.
Possible complications include:
- limb deformity;
- limp;
- transition of pain to a chronic form (in this case, they are present almost constantly);
- infringement of intra-articular bodies;
- Deep venous thrombosis;
- heterotopic ossification (formation of bone plates in soft tissues);
- osteoarthritis;
- contractures: impaired joint mobility;
- necrosis;
- pathological fractures.
Without treatment, pathologies can lead to persistent impairment of mobility, the inability to live a full life and even take care of oneself, and disability. With extensive purulent processes in the hip joint area, in the absence of treatment, infectious-toxic shock or sepsis may develop, which can be fatal.
Prevention
First of all, experts recommend leading a healthy lifestyle:
- move more, but do not overload the body with excessive training;
- control body weight to prevent obesity;
- eat a nutritious and varied diet (nutrition should be balanced in terms of basic macro- and micronutrients, as well as total caloric content);
- Do not use systemic medications without a doctor's prescription.
For people who, due to their professional activities, are forced to spend a lot of time on their feet, it is advisable to periodically rest the body and undergo preventive examinations by an orthopedist-traumatologist at least once a year.
Patients with diseases of the musculoskeletal system should be under dispensary observation, strictly follow medical instructions and monitor their condition.
To prevent injuries to the hip joint, it is recommended to avoid extreme sports, use protective equipment when exercising, and do not perform complex exercises without the necessary skills and physical training.
It is advisable for older people to move very carefully in icy conditions and not go outside unless absolutely necessary.
Treatment of hip pain in a professional clinic.
The doctors of the multidisciplinary center are top-level specialists with the necessary practical skills and extensive knowledge in various fields of medicine. They consider the patient's problem individually, drawing up a diagnostic and treatment program taking into account all health characteristics. Specialists use an integrated approach to solve a variety of health problems. They not only eliminate a specific symptom, but also try to identify and eliminate its cause, obvious and non-obvious consequences. Only in this way can the patient's health be fully restored, giving him the opportunity to live a normal life, to move without pain or restrictions.
When seeking medical help from the doctors of the clinic, everyone has the right to count on the friendly attitude of specialists and junior staff, assistance in rehabilitation and objectivity.